In Previous post, we have discussed about Agile Overview: what is
agile, agile manifesto, agile principles and classification of agile
methodologies into Light weight approaches and fuller approaches.
Light weight approaches: Scrum, Lean, Kanban, Crystal and Extreme
programming (XP)
Fuller Approaches: DSDM (Dynamic systems development method), AUP
(Agile unified process) and FDD (Feature driven development)
Let’s discuss about one of the Light weight approaches in this post.
Let’s get started with Scrum. Before getting started with scrum just wanted to
know whether you believe in statement “None
of us is as strong as all of us”. Please continue reading if your answer is ‘YES’ else, read this post twice to realize what wonders can be done
if you work in a team.
What is
Scrum?
Scrum has become terrifically popular over the past few years due to its
simplicity, productivity and broad applicability
First definition of Scrum:
Scrum was first defined as "a
flexible, holistic product development strategy where a development team works
as a unit to reach a common goal" as opposed to a "traditional, sequential approach"
in 1986 by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka in the "New New Product Development Game"
According to the Scrum Alliance,
“Scrum is an agile framework for
completing complex projects. Scrum originally was formalized for software
development projects, but works well for any complex, innovative scope of work.
The possibilities are endless. The Scrum framework is deceptively simple”
Scrum is a better way of working for teams to work together to develop
a product. Product gets developed in small pieces (Called as Product increment
in Scrum) and it is delivered as integration to the main product. As team is
working on small piece of the product, it gives scope to be more focused (to
build exactly and only what is needed), creative and enables better change
management
To be more simple and specific, “Scrum
is a framework for effective team & customer collaboration to deal with
complex projects. It is originally designed for software development work but
it can be used to any work if you feel appropriate”
Scrum
values
The Agile
Manifesto values apply directly to Scrum
Individuals and
interactions over processes and tools
Working software
over comprehensive documentation
Customer
collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change
over following a plan
All activities performed in scrum are based on above agile manifesto
and scrum values. Team needs to practice these to achieve effective team work
and continuous improvement. The scrum values
are Commitment, Courage, Focus, Openness and Respect
Scrum
Framework
Scrum
framework consist Scrum roles, Scrum
Ceremonies/Activities, Scrum Artifacts and Scrum Rules.
Scrum Roles: Scrum Team includes 3
roles
Scrum Master (SM)
Product Owner (PO)
The members of the Development team
(DT)
Scrum Ceremonies: 5 activities in the
process of scrum which facilitates planning, execution, inspection and
adaptation
Product backlog refinement meeting
Sprint Planning Meeting
Daily Scrum Meeting
Sprint Review Meeting
Sprint Retrospective Meeting
Scrum Artifacts: Scrum team has 3
artifacts
Product backlog
Sprint Backlog
Product Increment
Scrum Rules
Before discussing scrum framework one by one, let’s take a look at Scrum framework quickie. After getting to
know about scrum, I have seen many pictures explaining scrum. But I felt those
pictures are not providing full information about scrum and they are meant for
people who have prior knowledge of scrum. Thus made below picture based on my
scrum understanding
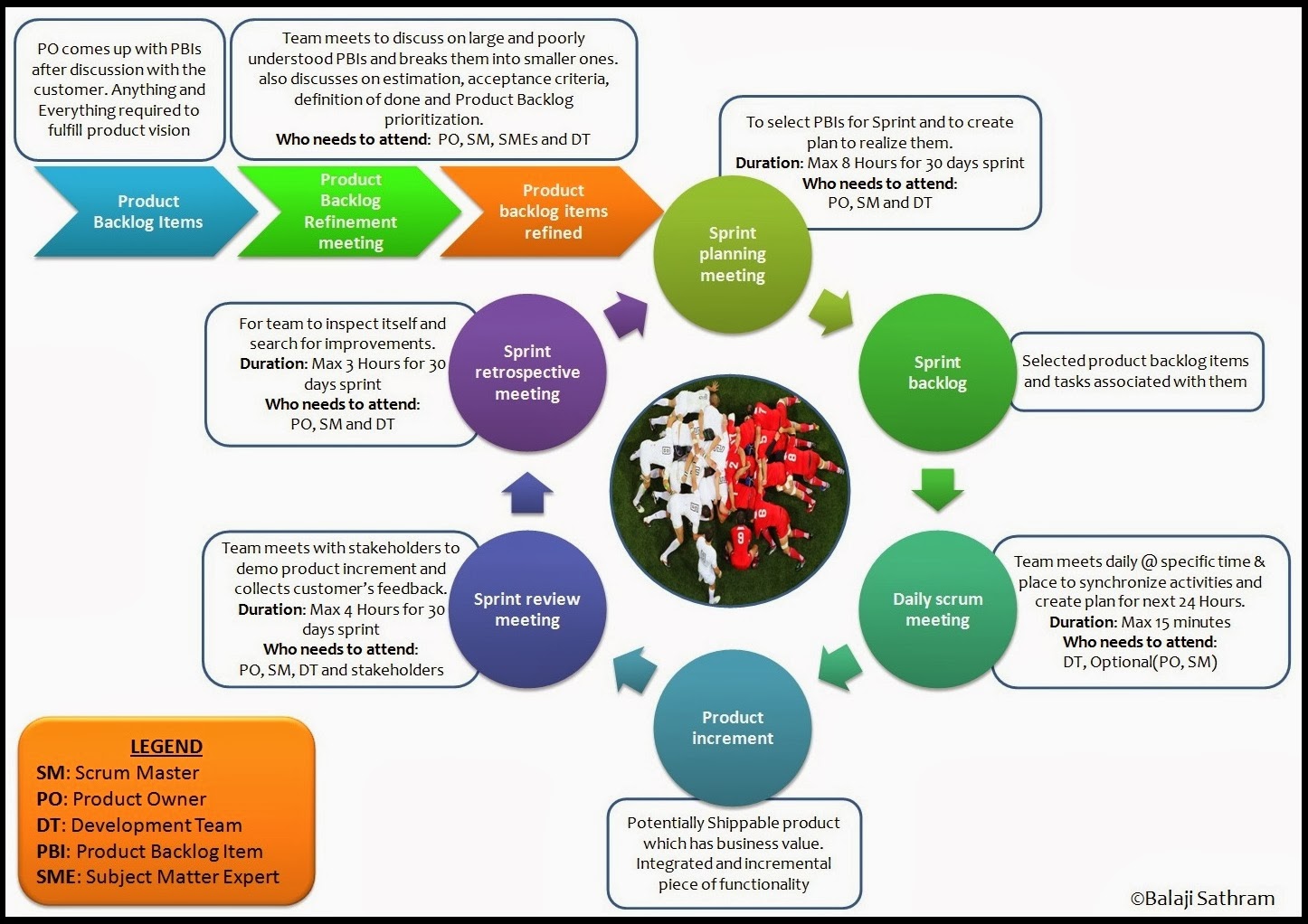
Scrum Framework Quickie:
ü
In Scrum, work is performed in SPRINTs. Sprint
is the basic unit of scrum development.
It is “Time-Boxed” effort i.e. restricted to a specific duration. The
duration is decided by the team (normally 1week to 1month)
ü
Sprint is protected with respect to team, Goal
and Length. SPRINT Starts with planning meeting and ends with Sprint
retrospective meeting
ü
Product owner discusses with customer and comes
up with list of high-level requirements (Product Backlog)
ü
Product owner explains requirements to the scrum
team, High-level requirements are broken in to smaller features by grooming
process and these features are prioritized based on business value (Product
Backlog Refinement Meeting)
ü
Before starting the sprint, scrum team meets and
selects the tasks to work in next sprint and comes up with a list called Sprint
Backlog (Sprint Planning Meeting)
ü
Scrum team starts working on the sprint goal.
Team meets daily at specific place & time to synchronize team activities
(Daily Scrum meeting)
ü
Scrum team meets with customer to show-case/demo
the features they developed (Product Increment) and collects customer feedback
(Sprint Review Meeting)
ü
Scrum team meets to inspect self and search for
improvements on anything and everything related to team (Sprint Retrospective
Meeting)
ü
Sprint Closure…Plan for next sprint
Hope you got a fair idea on how scrum works by now. Let’s dive in deep
and learn about scrum framework in detail
Scrum Roles
Scrum master:
Scrum master helps the scrum team to work together efficiently towards
the sprint goal; Ensures scrum process is followed as intended and educates the
team on scrum process (Team Scrum’s expert).
Protects the team from external distractions and removes team
impediments if any. The Servant-Leader (Servant first, Leads the team next)
Ideally this should not be played by line manager. But if a line
manager can honestly play scrum master’s role by keeping everything aside, then
why not? (Just think about it)
Facilitates all activities in scrum, Helps team to focus on
identifying a meaningful functionality that can be achieved in the sprint in
the order of product backlog priority
Product Owner:
Product owner is the voice of the customer and represents
stakeholders. Accountable for ensuring that team delivers value to the business
by product backlog management (prioritizing product backlog before each sprint,
adding new things to the product backlog, refines product backlog and
communicates customer requirements to the team)
Defines product features; Responsible for Project management, Product
management and Product marketing. PO acts as a bridge between Customer and the
scrum team and is at least 50% available to the scrum team
Responsible for ROI (Return on Investment), optimizes the business
value of the work done by scrum team. PO is responsible for project schedule,
project cost tracking & Estimation, change management
Explains customer requirements to the team and clarifies their doubts
if any. PO accepts or rejects the sprint deliverables based on the defined
acceptance criteria. PO needs to accept the product increment before it reaches
the customer
PO in release planning: Creates project management plan, Responsible
for determining the release dates by tracking team’s performance matrices.
The Members of the Development Team:
Team which turns the product backlog into product increment
(Potentially shippable product); Cross functional team who do the actual
product development. Involves different roles i.e. Business analyst, UX Expert,
Programmer, Database administrator, Release Engineer, Technical Architect, Tester,
Technical Writer, User Interface Specialist, Quality Assurance, Developer and
any other role required for delivering product increment
Autonomous and self-organizing team, Size is ideally considered as 7±2,
who works full time
Selects the refined requirements to deliver in Sprint, divides the
selected stories into tasks, Estimates work and decide how many stories will be
delivered by end of sprint and finally commits to Sprint goal
Creates work breakdown structure, Determine how team accomplishes work
Demonstrates product increment to the customers in sprint review
meeting and releases to the customers
Scrum
Ceremonies
Product backlog refinement meeting:
It is an ongoing process for reviewing product backlog items (PBIs),
main objective of this meeting is to keep backlog ready for next 2 sprints by
creating, refining, estimating and prioritizing PBIs. Duration and frequency of
the meeting is decided by the scrum team.
Product backlog consists of User Stories (Something which user wants),
Epics (Big User story) and Themes (Bigger User story)
Large PBIs gets broken down in to smaller user stories which makes
them clear and executable for teams once they pick these for sprint execution
Enrich PBIs with new details and Re-Prioritize PBIs based on the
business scope
Sprint Planning Meeting:
Meeting is held at beginning of the sprint cycle to select refined
PBIs to be done for the sprint.
Meeting duration is 8 hours for 30 days sprint
Attendees for this meeting: DT, SM and PO
It is maximum 8 Hours for 30days sprint. First 4 hours are spent on
team discussion for prioritizing the product backlog. Next 4 hours are spent on
DT making a plan for the sprint
It results in Sprint Backlog (List of PBIs selected to be done in the
sprint)
Daily Scrum Meeting:
Daily scrum meeting occurs each day during the sprint. DT meets @
specific time & place to synchronize activities in the team.
Meeting duration is time-boxed up to 15
minutes
Attendees for this meeting: DT, Optional
(SM, PO)
It has certain guidelines mentioned below
DT needs to come
prepared with updates
Starts by specific
time even if some team member is missing
DT tells about three
things
What have you done
from yesterday’s daily scrum today’s daily scrum?
What are you
planning to do from today’s daily scrum to tomorrow’s daily scrum?
Are there any
impediments blocking your work progress?
Scrum master makes a
note of impediments and works towards resolving it outside the meeting. No
detailed discussions happens in this meeting
Sprint Review Meeting:
Sprint review meeting is held at the end of a sprint cycle. Scrum team
reviews the work completed and the planned work which is not completed.
Scrum team demos completed work (Product increment/Potentially
shippable product) to internal and external stakeholders. Stakeholders review
the product increment and provide feedback to the scrum team
Duration: Max 4 Hours
for 30 days sprint
Attendees for this
meeting would be SM, PO, DT and Stakeholders
Product owner makes a note of the stakeholder’s feedback and
adds/changes PBIs based on the same
Sprint Retrospective Meeting:
Sprint retrospective meeting is held at the end of a sprint cycle.
This meeting is for team to inspect itself and search for improvements
Duration: Max 3 Hours
for 30 days sprint
Attendees for this
meeting would be SM, DT and PO
Team gathers data of what worked well and what needs improvement in
the past sprint with regard to product, process and what not, everything
related to scrum team
Scrum master asks questions to the team and generate insights based on
the data provided by the team
Team creates a list of Action items and prioritizes the action items
based on team voting agreement
Request volunteer owner for action items and volunteers will be
responsible for that action item once it is assigned
Scrum
Artifacts
After going through scrum ceremonies, you might have got an idea of
scrum artifacts as well. Let’s see them in detail
Product backlog:
List of product requirements in a prioritized order, priority of
product backlog items is done by product owner based on business value, risk
and dependencies etc
Product backlog consists of features, Bug fixes, non functional
requirements, anything and everything required to fulfill product vision
Product backlog is open and any one can change it but product is
responsible for prioritizing them based on discussions with customer
Usually, PBIs are in user story format
As a <WHO|ROLE>
I want <WHAT|FEATURE>
So that <WHY|PURPOSE>
Each PBI contains business value, DT effort estimation i.e.
estimations are given as story points as unit. Story points should be from
Fibonacci sequence. These estimations will help PO in release planning
Estimations given by DT team should be either story points or
estimated hours of effort to complete the task
Sprint Backlog:
Sprint backlog is a list of product backlog items selected for the next
sprint & associated tasks and this has been derived from top list items of
product backlog
DT selects PBIs based on the past sprint velocity if available or else
dive and swim if it is first sprint of a new project
PBIs are broken down in to tasks by the DT. DT team members chooses
the tasks based on their skill set which is a part of self-organization of the
DT
These are written on sticky notes and pasted on a board under
categories “To do”, “In Progress” and “Done”
No additional items can be added to sprint backlog once it is committed.
Only DT is allowed to make changes for sprint backlog if needed
Once Sprint goal is achieved, scrum team analyses product backlog and
go for next set of items for next sprint
Product Increment:
Product increment is nothing but potentially shippable product
completed during the sprint. At the end of the sprint product increment needs
to fulfill “Definition of DONE” criteria (also called as EXIT criteria).
According to scrum.org, “Definition of Done” is a shared understanding
of what it means for work to be complete, to ensure transparency
Definition of done is defined by scrum team. If product increment
needs to be deployed to the user, then it should complete all the criteria
pre-defined by the team
Example of Definition of DONE criteria: Analyzed, Designed, Implemented,
Reviewed, Tested, Packaged, Automated, Deployed, Integrated, Accepted by PO, No
known BUGS and Got feedback from Customer
Once the product increment is passed through EXIT criteria, it should
be in usable condition irrespective of whether PO is releasing it or not
Scrum Rules
Whatever we have been discussing in this post, all are scrum rules. Officially,
the Scrum Guide is the Scrum rulebook maintained by Scrum.org,
Ken Schwaber, and Jeff Sutherland. Please download your copy here
and go through it
Apart from Scrum roles, Scrum ceremonies and Scrum artifacts in Scrum
framework, you need to know some commonly used scrum terminology.
Sprint Burn-down chart: Sprint
Burn-down chart is a graphical representation to track sprint progress. Shows remaining work in the sprint
backlog. Number of days in the sprint is
taken on X-axis and Number of hours OR Number of story points is taken on
Y-axis to plot the graph. Sample graph is given below
Release Burn-down chart: Release
Burn-down chart is a graphical representation to track release progress. It
shows the amount of work left to complete to reach release target. Number of
sprints is taken on the X-axis and On Y-axis, it is up to the team to decide.
It can be Story points, Team days or ideal days.
Scrum task board: Team
members lists the tasks of the sprint under the categories “To do”, “In
Progress”, “Done” in a big board which is called as scrum task board and
updates the tasks on daily basis. Ideally before attending the daily scrum
meeting
Team Velocity: The number
of story points (Product backlog effort) completed in one sprint is considered
as team velocity
Abnormal Termination: When
product owner realizes that it makes no sense or business value to continue
sprint, PO can cancel the sprint at any point of sprint duration is called
abnormal termination. Inputs for this process can be given by SM, DT or
management
Spike: SPIKE is a technical
investigation or collecting more information with respect to one task. It can
have maximum time box size of one sprint. For more information on spikes click here
ScrumBut: It is an
exception to the pure scrum methodology. Scrum framework which has been changed
based on the needs is called ScrumBut
Technical Debt: (also known
as Design Debt or Code Debt). The debt is a particular task that needs to be
done before it is considered as complete in codebase. If it is not repaid
(Fixed) in the early stage, it accumulates eventually making it hard implement
later on
With this we have completed scrum framework. Let us look at advanced
scrum concepts in posts after completing agile methodologies. Thank you for
stopping by and reading my blog, it means a lot to me. Help me to improve by giving your feedback. I appreciate it very much!
Please feel free to reach out to me
Linkedin: http://in.linkedin.com/in/sathrambalaji
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/sathrambalaji

No comments:
Post a Comment